1203. Sort Items by Groups Respecting Dependencies
Question
There are n items each belonging to zero or one of m groups where group[i] is the group that the i-th item belongs to and it's equal to -1 if the i-th item belongs to no group. The items and the groups are zero indexed. A group can have no item belonging to it.
Return a sorted list of the items such that:
- The items that belong to the same group are next to each other in the sorted list.
- There are some relations between these items where
beforeItems[i]is a list containing all the items that should come before thei-th item in the sorted array (to the left of thei-th item).
Return any solution if there is more than one solution and return an empty list if there is no solution.
Example 1:
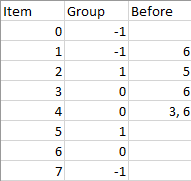
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[|],[6],[5],[6],[3,6],[],[],[]]
Output: [6,3,4,1,5,2,0,7]
Example 2:
Input: n = 8, m = 2, group = [-1,-1,1,0,0,1,0,-1], beforeItems = [[],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[|],[6],[5],[6],[3],[],[4],[]]
Output: []
Explanation: This is the same as example 1 except that 4 needs to be before 6 in the sorted list.
Constraints:
1 <= m <= n <= 3 * 104group.length == beforeItems.length == n-1 <= group[i] <= m - 10 <= beforeItems[i].length <= n - 10 <= beforeItems[i][j] <= n - 1i != beforeItems[i][j]beforeItems[i]does not contain duplicates elements.
Approach 1: Kahn's topo sort
Intuition
- We must respect item dependencies AND keep items of the same group together.
- Dependencies between items in different groups imply a dependency between those groups.
- Therefore:
- Topologically sort groups.
- Topologically sort items.
- Arrange items inside their group according to item-topo.
- Output groups in group-topo order to keep each group contiguous.
Algorithm
- Assign group IDs
For items withgroup[i] == -1, give them unique new group IDs. - Build item graph
For each dependencya → bfrombeforeItems, add edgea → b. - Build group graph
Ifgroup[a] != group[b], add edgegroup[a] → group[b]. - Topological sort groups
- If cycle → return empty list.
- Topological sort items
- If cycle → return empty list.
- Bucket items by group
- Traverse items in item-topo order.
- For item
x, push intoitemsInGroup[group[x]].
- Build final list
- For each group in group-topo order, append its bucket of items.
Code
class Solution {
public:
// Standard Kahn's topological sort
vector<int> topoSort(vector<vector<int>>& adj, vector<int>& indegree) {
queue<int> q;
int n = adj.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) q.push(i);
}
vector<int> topo;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
topo.push_back(u);
for (int v : adj[u]) {
indegree[v]--;
if (indegree[v] == 0) q.push(v);
}
}
if (topo.size() != n) return {}; // cycle → fail
return topo;
}
vector<int> sortItems(int n, int m, vector<int>& group, vector<vector<int>>& beforeItems) {
// 1. assign new groups to all items with group[i] == -1
int newGroupId = m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (group[i] == -1) {
group[i] = newGroupId++;
}
}
int G = newGroupId; // total groups now
// 2. Build graphs
vector<vector<int>> itemAdj(n);
vector<int> itemIndegree(n, 0);
vector<vector<int>> groupAdj(G);
vector<int> groupIndegree(G, 0);
// fill graphs
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
for (int prev: beforeItems[i]) {
itemAdj[prev].push_back(i);
itemIndegree[i]++;
int gPrev = group[prev];
int gCurr = group[i];
if (gPrev != gCurr) {
groupAdj[gPrev].push_back(gCurr);
groupIndegree[gCurr]++;
}
}
}
// 3. topological sort on groups
vector<int> groupOrder = topoSort(groupAdj, groupIndegree);
if (groupOrder.empty()) return {};
// 4. topo sort on items
vector<int> itemOrder = topoSort(itemAdj, itemIndegree);
if (itemOrder.empty()) return {};
// 5. bucket items by group, in item topo order
vector<vector<int>> itemsInGroup(G);
for (int item: itemOrder) {
itemsInGroup[group[item]].push_back(item);
}
// 6. build final result using group topo order
vector<int> ans;
for (int g: groupOrder) {
for (int item: itemsInGroup[g]) {
ans.push_back(item);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
n= number of itemsg= number of groups (after adding new ones)E= total item dependencies