1514. Path with Maximum Probability
Question
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
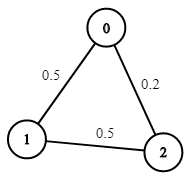
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2|0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.25000
Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
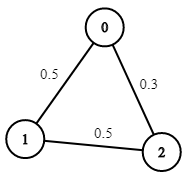
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2|0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
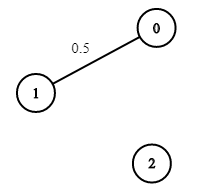
Input: n = 3, edges = 0,1, succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2
Output: 0.00000
Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
Approach 1: Dijkstra
Intuition
- This is Dijkstra’s algorithm, but instead of minimizing sum of weights, we maximize the product of probabilities.
- A higher-probability path is “better,” so we use a max-heap and relax edges by multiplying probabilities instead of adding weights.
Algorithm
- Build an adjacency list: for each edge
(u, v, p), add(p, v)and(p, u). - Maintain
maxProb[i]= highest probability found so far to reach nodei. - Use a max-heap storing
(probability, node)starting with(1.0, start). - Pop the node with the highest probability.
- If it’s the target, return the probability.
- For each neighbor:
- Compute
newProb = curProb * edgeProb. - If
newProb > maxProb[neighbor], update and push neighbor into the heap.
- Compute
- If the end is never reached, return
0.
Code
class Solution {
public:
double maxProbability(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges,
vector<double>& succProb, int start, int end) {
unordered_map<int, vector<pair<double, int>>> graph;
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) {
int u = edges[i][0], v = edges[i][1];
double pathProb = succProb[i];
graph[u].push_back({pathProb, v});
graph[v].push_back({pathProb, u});
}
vector<double> maxProb(n, 0.0);
maxProb[start] = 1.0;
// please note that the priority queue in c++ is a max heap by default
// and the sorting is decided by the first element of the pair.
priority_queue<pair<double, int>> pq;
pq.push({1.0, start});
while (!pq.empty()) {
double curProb = pq.top().first;
int curNode = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (curNode == end) {
return curProb;
}
if (!graph[curNode]
.empty()) { // Check if the node has been processed
for (auto& nxt : graph[curNode]) {
int nxtNode = nxt.second;
double pathProb = nxt.first;
if (curProb * pathProb > maxProb[nxtNode]) {
maxProb[nxtNode] = curProb * pathProb;
pq.push({maxProb[nxtNode], nxtNode});
}
}
graph[curNode]
.clear(); // Clear the adjacency list by removing the entry
}
}
return 0.0;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
-
Time Complexity:
- Building graph: O(E)
- Dijkstra with a binary heap: O(E log V) (each edge relaxes at most once with a heap push/pop)
-
Space Complexity:
- Graph storage: O(E)
- Probability array + heap: O(V)
- Total: O(V + E)