1631. Path With Minimum Effort
Question
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route's effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
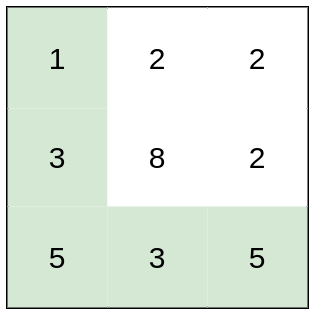
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5|1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
Output: 2
Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells.
This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
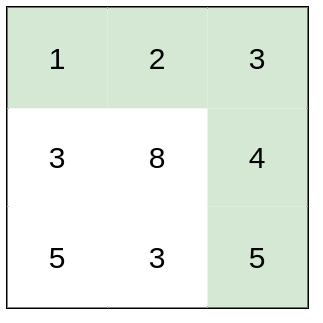
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5|1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
Output: 1
Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
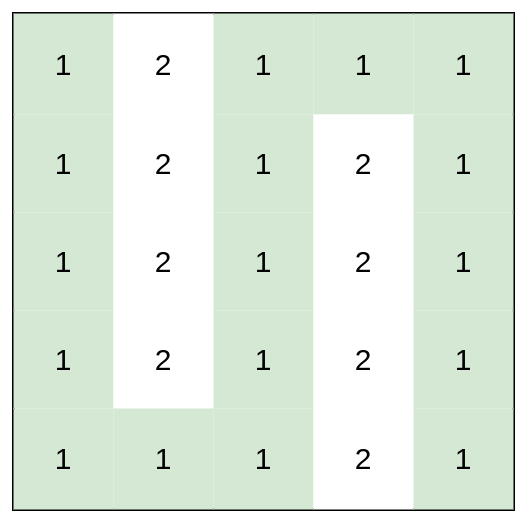
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1|1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]]
Output: 0
Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- Using pair as node for Dijkstra
Algorithm
- Convert heights grid to adj matrix
- Dijkstra's algorithm, instead of addition of weights we are just getting the max of the new distance and current distance
Code
class Solution {
public:
int minimumEffortPath(vector<vector<int>>& heights) {
// 0. convert adj matric to adj list
vector<vector<int>> directions = {
{-1, 0},
{0, -1},
{1, 0},
{0, 1}
};
auto hash_pair = [](const std::pair<int, int>& p) {
return std::hash<int>{}(p.first) ^ std::hash<int>{}(p.second);
};
int rows = heights.size(), cols = heights[0].size();
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<pair<int, int>,int>>, decltype(hash_pair)> adj;
for (int i = 0 ; i < rows ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < cols ; j++) {
int r = i;
int c = j;
if (adj.find({r, c}) == adj.end()) {
adj[{r, c}] = {};
}
for (auto& direction: directions) {
int nr = r + direction[0];
int nc = c + direction[1];
if (nr < 0 || nr >= rows || nc < 0 || nc >= cols ) {
continue;
}
int absDiff = abs(heights[r][c] - heights[nr][nc]);
adj[{r, c}].push_back({{nr, nc}, absDiff});
}
}
}
// 1. dijkstra
priority_queue<
pair<int, pair<int,int>>,
vector<pair<int, pair<int,int>>>,
greater<pair<int, pair<int,int>>>
> pq;
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, int, decltype(hash_pair)> dist;
for (int i = 0 ; i < rows ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < cols ; j++) {
dist[{i, j}] = INT_MAX;
}
}
pq.push({0, {0, 0}});
dist[{0, 0}] = 0;
while(!pq.empty()) {
auto node = pq.top().second;
auto currDist = pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
for (auto it: adj[node]) {
auto neighbor = it.first;
auto weight = it.second;
int newDist = max(currDist, weight);
if (newDist < dist[neighbor]) {
dist[neighbor] = newDist;
pq.push({newDist, neighbor});
}
}
}
return dist[{rows - 1, cols - 1}];
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Better
Intuition
Algorithm
Code
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 3: Optimal
Intuition
Algorithm
Code
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: