19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Question
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
Example 1:
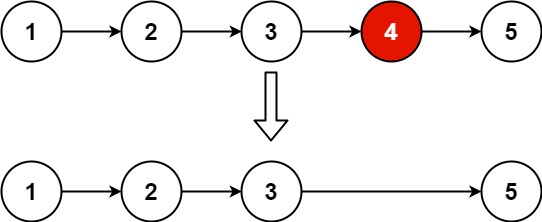
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1], n = 1
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,2], n = 1
Output: [1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
sz. 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
Follow up: Could you do this in one pass?
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- Calculate the total size
Algorithm
- Edge case:
if (head == NULL) return head - Declare & initialize
int count = 0,ListNode* curr = head - Loop through LL using
curr& increment count by 1 in each iteration - Edge case:
if (count == n)- Declare & initialize
ListNode* toDeltohead - Declare & initialize
ListNode* newHead = head->next - Delete toDel
- Return
newHead
- Declare & initialize
- Calculate the index of the node to be deleted
res = count - 1 - Reinitialize
currtohead - Loop through LL using
curr- Decrement
resby 1 - Check
if (res == 0) break; curr = curr->next
- Decrement
ListNode* toDel = curr->next- Change links
curr->next = curr->next->next - Delete
toDel - Return
head
Code
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (head == NULL) {
return head;
}
int count = 0;
ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr) {
count++;
curr = curr->next;
}
if (count == n) {
ListNode* toDel = head;
ListNode* newHead = head->next;
delete toDel;
return newHead;
}
int res = count - n;
curr = head;
while (curr) {
res--;
if (res == 0) {
break;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
ListNode* toDel = curr->next;
curr->next = curr->next->next;
delete toDel;
return head;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Optimal
Algorithm
- Edge Case Check:
- If the list is empty (
head == NULL), returnNULL.
- If the list is empty (
- Initialize Two Pointers:
- Create two pointers,
fastandslow, both initially pointing to thehead.
- Create two pointers,
- Advance the
fastPointer:- Move the
fastpointer nnn steps forward in the list. - If
fastbecomesNULLafter this step, it means the nnn-th node from the end is thehead. Remove theheadand returnhead->next.
- Move the
- Move Both Pointers:
- Simultaneously move the
fastandslowpointers one step at a time untilfast->nextbecomesNULL. - At this point, the
slowpointer will be just before the node to be removed.
- Simultaneously move the
- Delete the Node:
- Save a reference to the node to be removed (
toDel = slow->next). - Update
slow->nextto skip the node (slow->next = slow->next->next).
- Save a reference to the node to be removed (
- Free Memory:
- Delete the node referenced by
toDel.
- Delete the node referenced by
- Return the Updated List:
- Return the
headof the updated list.
- Return the
Code
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* slow = head;
// Move fast pointer n steps ahead
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
fast = fast->next;
}
// If fast is null, the node to remove is the head
if (!fast) {
ListNode* toDel = head;
head = head->next;
delete toDel;
return head;
}
// Move both pointers until fast reaches the end
while (fast->next) {
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
// Remove the nth node
ListNode* toDel = slow->next;
slow->next = slow->next->next;
delete toDel;
return head;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: