2192. All Ancestors of a Node in a Directed Acyclic Graph
Question
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive).
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] denotes that there is a unidirectional edge from fromi to toi in the graph.
Return a list answer, where answer[i] is the list of ancestors of the ith node, sorted in ascending order.
A node u is an ancestor of another node v if u can reach v via a set of edges.
Example 1:
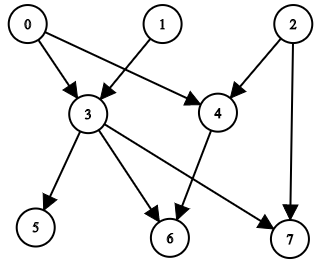
Input: n = 8, edgeList = [[0,3],[0,4],[1,3],[2,4],[2,7],[3,5],[3,6],[3,7],[4,6|0,3],[0,4],[1,3],[2,4],[2,7],[3,5],[3,6],[3,7],[4,6]]
Output: [[],[],[],[0,1],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,2,3|],[],[],[0,1],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation:
The above diagram represents the input graph.
- Nodes 0, 1, and 2 do not have any ancestors.
- Node 3 has two ancestors 0 and 1.
- Node 4 has two ancestors 0 and 2.
- Node 5 has three ancestors 0, 1, and 3.
- Node 6 has five ancestors 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4.
- Node 7 has four ancestors 0, 1, 2, and 3.
Example 2:
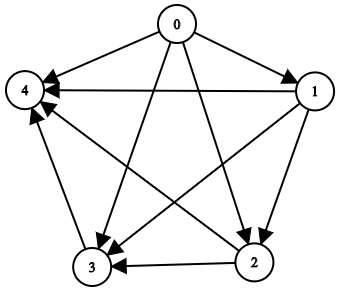
Input: n = 5, edgeList = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,4|0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,4]]
Output: [[],[0],[0,1],[0,1,2],[0,1,2,3|],[0],[0,1],[0,1,2],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation:
The above diagram represents the input graph.
- Node 0 does not have any ancestor.
- Node 1 has one ancestor 0.
- Node 2 has two ancestors 0 and 1.
- Node 3 has three ancestors 0, 1, and 2.
- Node 4 has four ancestors 0, 1, 2, and 3.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10000 <= edges.length <= min(2000, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 20 <= fromi, toi <= n - 1fromi != toi- There are no duplicate edges.
- The graph is directed and acyclic.
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- For each node, we want all its ancestors (all nodes that can reach it).
- Process nodes in topological order, so when we handle a node
curr, we already know all its ancestors. - Maintain
table[child][ancestor] = true.- For each edge
curr → neighbor:curris a direct ancestor ofneighbor.- Every ancestor of
curris also an ancestor ofneighbor(transitive propagation).
- For each edge
Algorithm
- Build graph + indegree
- Create adjacency list
adjfromedges. - Compute
indegreeof each node.
- Create adjacency list
- Topological sort (Kahn)
- Push all nodes with
indegree == 0into a queue.
- Push all nodes with
- DP over topo order
- Initialize
table[n][n] = false. - While queue not empty:
- Pop
curr. - For each
neighborinadj[curr]:- Mark direct ancestor:
table[neighbor][curr] = true. - For all
i:- If
table[curr][i]is true, thentable[neighbor][i] = true
(every ancestor ofcurris ancestor ofneighbor).
- If
- Decrease
indegree[neighbor]; if it becomes 0, push it.
- Mark direct ancestor:
- Pop
- Initialize
- Build answer
- For each node
i:- Collect all
jwheretable[i][j] == trueinto a sorted listanswer[i].
- Collect all
- Return
answer.
- For each node
Code
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> getAncestors(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> adj(n, vector<int>());
vector<int> indegree(n, 0);
for (int i = 0 ; i < edges.size() ; i++) {
vector<int> edge = edges[i];
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
adj[u].push_back(v);
indegree[v]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
vector<vector<bool>> table(n, vector<bool>(n, false));
while(!q.empty()) {
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto neighbor: adj[curr]) {
table[neighbor][curr] = true;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (table[curr][i]) {
table[neighbor][i] = true;
}
}
indegree[neighbor]--;
if (indegree[neighbor] == 0) {
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
vector<vector<int>> answer(n, vector<int>());
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
for (int j = 0 ; j < n ; j++) {
if (table[i][j]) {
answer[i].push_back(j);
}
}
}
return answer;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: