2392. Build a Matrix With Conditions
Question
You are given a positive integer k. You are also given:
- a 2D integer array
rowConditionsof sizenwhererowConditions[i] = [abovei, belowi], and - a 2D integer array
colConditionsof sizemwherecolConditions[i] = [lefti, righti].
The two arrays contain integers from 1 to k.
You have to build a k x k matrix that contains each of the numbers from 1 to k exactly once. The remaining cells should have the value 0.
The matrix should also satisfy the following conditions:
- The number
aboveishould appear in a row that is strictly above the row at which the numberbelowiappears for allifrom0ton - 1. - The number
leftishould appear in a column that is strictly left of the column at which the numberrightiappears for allifrom0tom - 1.
Return any matrix that satisfies the conditions. If no answer exists, return an empty matrix.
Example 1:
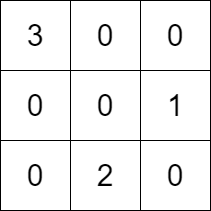
Input: k = 3, rowConditions = [[1,2],[3,2|1,2],[3,2]], colConditions = [[2,1],[3,2|2,1],[3,2]]
Output: [[3,0,0],[0,0,1],[0,2,0|3,0,0],[0,0,1],[0,2,0]]
Explanation: The diagram above shows a valid example of a matrix that satisfies all the conditions.
The row conditions are the following:
- Number 1 is in row 1, and number 2 is in row 2, so 1 is above 2 in the matrix.
- Number 3 is in row 0, and number 2 is in row 2, so 3 is above 2 in the matrix.
The column conditions are the following: - Number 2 is in column 1, and number 1 is in column 2, so 2 is left of 1 in the matrix.
- Number 3 is in column 0, and number 2 is in column 1, so 3 is left of 2 in the matrix.
Note that there may be multiple correct answers.
Example 2:
Input: k = 3, rowConditions = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,1],[2,3|1,2],[2,3],[3,1],[2,3]], colConditions = 2,1
Output: []
Explanation: From the first two conditions, 3 has to be below 1 but the third conditions needs 3 to be above 1 to be satisfied.
No matrix can satisfy all the conditions, so we return the empty matrix.
Constraints:
2 <= k <= 4001 <= rowConditions.length, colConditions.length <= 104rowConditions[i].length == colConditions[i].length == 21 <= abovei, belowi, lefti, righti <= kabovei != belowilefti != righti
Approach 1: Kahn's algorithm (topo sort bfs)
Intuition
- Each number 1..k must appear in the matrix exactly once.
- Row conditions give a partial order for rows; column conditions give a partial order for columns.
- If both partial orders are valid DAGs, we get:
- a topological order for rows,
- a topological order for columns.
- Place each number at the intersection of its row-order index and column-order index.
Algorithm
- Build graph for row conditions and run topological sort.
If topo is invalid (cycle), return empty matrix. - Build graph for column conditions and run topological sort.
If topo invalid, return empty matrix. - Create:
posRow[x]= position ofxin row topo,posCol[x]= position ofxin column topo.
- Create a
k × kmatrix filled with0. - For each number
xfrom1..k, place it at:matrix[posRow[x]][posCol[x]] = x - Return the matrix.
Code
class Solution {
public:
// Returns a topological ordering of 1..k based on given edges.
// If it's impossible (cycle), returns an empty vector.
vector<int> getTopo(vector<vector<int>>& edges, int k) {
// graph[i] = list of nodes that come after i
vector<vector<int>> graph(k + 1);
vector<int> indegree(k + 1, 0);
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int from = edge[0];
int to = edge[1];
graph[from].push_back(to);
indegree[to]++;
}
queue<int> q;
// Nodes are 1..k
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
vector<int> topo;
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
topo.push_back(node);
for (int neighbor : graph[node]) {
indegree[neighbor]--;
if (indegree[neighbor] == 0) {
q.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
// If we didn't process all k nodes, there's a cycle → invalid
if ((int)topo.size() != k) return {};
return topo;
}
vector<vector<int>> buildMatrix(int k, vector<vector<int>>& rowConditions, vector<vector<int>>& colConditions) {
// Topological orderings for rows and columns
vector<int> topoRow = getTopo(rowConditions, k);
vector<int> topoCol = getTopo(colConditions, k);
// If either is impossible, return empty matrix
if (topoRow.empty() || topoCol.empty()) return {};
// posRow[x] = row index of number x
// posCol[x] = column index of number x
vector<int> posRow(k + 1), posCol(k + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
posRow[topoRow[i]] = i;
posCol[topoCol[i]] = i;
}
// Build k x k matrix, initially all zeros
vector<vector<int>> ans(k, vector<int>(k, 0));
// Place each number 1..k at its (row, col) position
for (int num = 1; num <= k; num++) {
int r = posRow[num];
int c = posCol[num];
ans[r][c] = num;
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
-
Time Complexity:
- Building graphs: O(k + m) for rows, O(k + m) for cols
(m = number of conditions) - Topological sort: O(k + m) twice
- Filling matrix: O(k)
Total: O(k + m)
- Building graphs: O(k + m) for rows, O(k + m) for cols
-
Space Complexity:
- Graphs + indegree arrays: O(k + m)
- Topo arrays + position arrays: O(k)
- Output matrix: O(k²)
Total: O(k²)