310. Minimum Height Trees
Question
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
Given a tree of n nodes labelled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of n - 1 edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the two nodes ai and bi in the tree, you can choose any node of the tree as the root. When you select a node x as the root, the result tree has height h. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height (i.e. min(h)) are called minimum height trees (MHTs).
Return a list of all MHTs' root labels. You can return the answer in any order.
The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
Example 1:
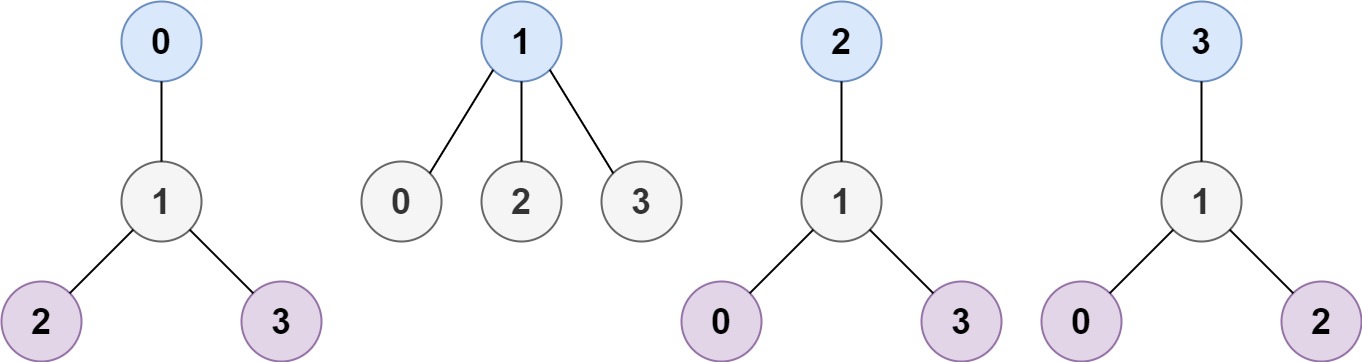
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,0],[1,2],[1,3|1,0],[1,2],[1,3]]
Output: [1]
Explanation: As shown, the height of the tree is 1 when the root is the node with label 1 which is the only MHT.
Example 2:
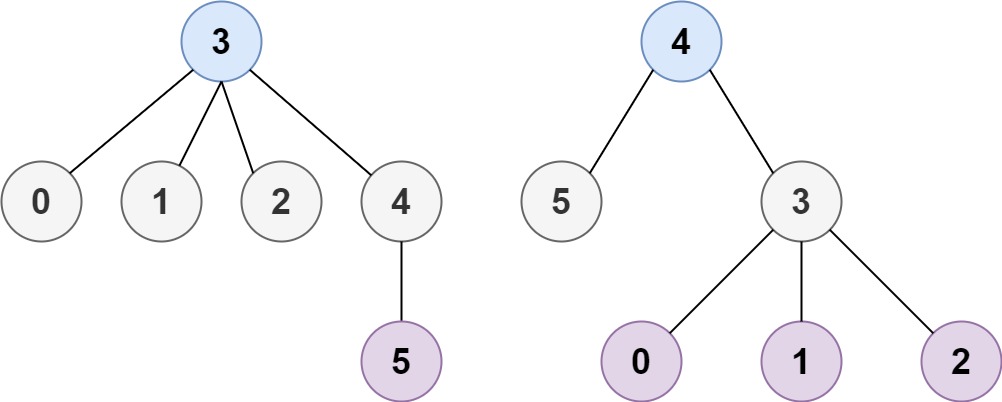
Input: n = 6, edges = [[3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4|3,0],[3,1],[3,2],[3,4],[5,4]]
Output: [3,4]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 2 * 104edges.length == n - 10 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- All the pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct. - The given input is guaranteed to be a tree and there will be no repeated edges.
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- Get max height for the graph from each node 559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
- Find out the min height
- Return all the nodes matching that min height
Algorithm
Code
class Solution {
public:
int getMaxHeight(int root, vector<vector<int>>& adj) {
int maxHeight = 1;
vector<bool> visited(adj.size(), false);
// node, depth
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({root, 1});
visited[root] = true;
while(!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front().first;
int currDepth = q.front().second;
q.pop();
maxHeight = max(currDepth, maxHeight);
for (auto neighbor: adj[node]) {
if (visited[neighbor] == false) {
q.push({neighbor, currDepth + 1});
visited[neighbor] = true;
}
}
}
return maxHeight;
}
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
// 0. converting edge list to adj list
vector<vector<int>> adj(n, vector<int>());
for (auto edge: edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
vector<int> maxHeight(n, 0);
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
maxHeight[i] = getMaxHeight(i, adj);
}
int minHeight = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
minHeight = min(minHeight, maxHeight[i]);
}
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (maxHeight[i] == minHeight) {
ans.push_back(i);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Optimal
Intuition
-
If we remove all the leaves, we will push towards the center
-
Logic
- A leaf can never be a minimum-height root. Its height is guaranteed worst-case.
- Any node directly connected to leaves is strictly more central.
- Remove leaves → update degrees → new leaves emerge.
- Iterate until the core stays. That core is the optimal root set.
-
Figure out how this relates to Topo Sort BFS Kahn's Algorithm DSA
Algorithm
Code
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
if (n == 1) return {0};
if (n == 2) return {0, 1};
// 0. converting edge list to adj list
vector<vector<int>> adj(n, vector<int>());
vector<int> degree(n, 0);
for (auto edge: edges) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
degree[u]++;
degree[v]++;
}
queue<int> leavesQueue;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (degree[i] == 1) {
leavesQueue.push(i);
}
}
int remaining = n;
while(remaining > 2) {
int currentLeafCount = leavesQueue.size();
remaining -= currentLeafCount;
while(currentLeafCount--) {
int leaf = leavesQueue.front();
leavesQueue.pop();
for (int neighbor: adj[leaf]) {
degree[neighbor]--;
if (degree[neighbor] == 1) {
leavesQueue.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
vector<int> ans;
while (!leavesQueue.empty()) {
ans.push_back(leavesQueue.front());
leavesQueue.pop();
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: