328. Odd Even Linked List
Question
Given the head of a singly linked list, group all the nodes with odd indices together followed by the nodes with even indices, and return the reordered list.
The first node is considered odd, and the second node is even, and so on.
Note that the relative order inside both the even and odd groups should remain as it was in the input.
You must solve the problem in O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) time complexity.
Example 1:
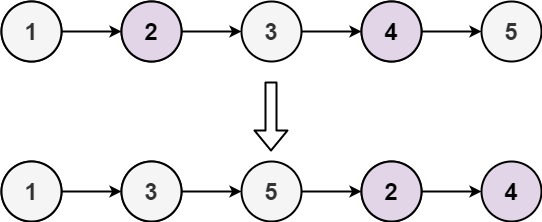
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [1,3,5,2,4]
Example 2:
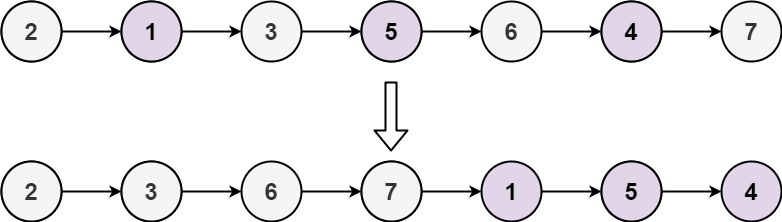
Input: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
Output: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the linked list is in the range
[0, 104]. -106 <= Node.val <= 106
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- Use an array
Algorithm
- Check for the edge case
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head - Declare
vector<int> arr - Declare & initialize
ListNode* curr = head - Loop through the linked list while
curr && curr->nextfor odd values- Add the val of
currnode toarr curr = curr->next->nextTo just get the odd values
- Add the val of
if (curr) ans.push_back(curr->val)- Reinitialize
curr = head->next - Loop through the linked list while
curr && curr->nextfor even values- Add the val of
currnode toarr curr = curr->next->nextTo just get the even values
- Add the val of
if (curr) ans.push_back(curr->val)- Loop through the linked list & replace the values of each node according to the array
- Return the head
Code
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
vector<int> arr;
ListNode* curr = head;
while (curr && curr->next) {
arr.push_back(curr->val);
curr = curr->next->next;
}
if (curr) {
arr.push_back(curr->val);
}
curr = head->next;
while (curr && curr->next) {
arr.push_back(curr->val);
curr = curr->next->next;
}
if (curr) {
arr.push_back(curr->val);
}
curr = head;
int i = 0;
while (curr) {
curr->val = arr[i++];
curr = curr->next;
}
return head;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Optimal
Algorithm
- Handle the edge case
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head - Declare & initialize
ListNode* oddCurr = head; - Declare & initialize
ListNode* evenCurr = head->next; - Declare & initialize
ListNode* evenHead = head->next;as we will loose reference to it when we change the evenCurr and need to link the odd to even - Loop through the LL
while (evenCurr && evenCurr->next)oddCurr->next = oddCurr->next->nextevenCurr->next = evenCurr->next->next- Increment
oddCurr,oddCurr = oddCurr->next - Increment
evenCurr,evenCurr = evenCurr->next
- Link odd list to even list
oddCurr->next = evenHead - return
head
Code
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* oddEvenList(ListNode* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode* oddCurr = head;
ListNode* evenCurr = head->next;
ListNode* evenHead = head->next;
while (evenCurr && evenCurr->next) {
oddCurr->next = oddCurr->next->next;
evenCurr->next = evenCurr->next->next;
oddCurr = oddCurr->next;
evenCurr = evenCurr->next;
}
oddCurr->next = evenHead;
return head;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
, Operation on each node - Space Complexity:
, No extra space