542. 01 Matrix
Question
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the distance of the nearest 0 for each cell.
The distance between two cells sharing a common edge is 1.
Example 1:
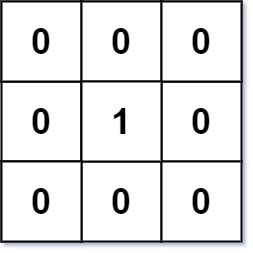
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0|0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0|0,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Example 2:
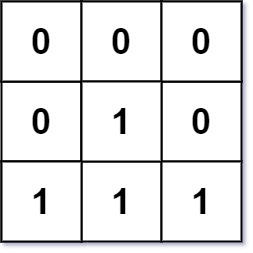
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1|0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]]
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1|0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,2,1]]
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1041 <= m * n <= 104mat[i][j]is either0or1.- There is at least one
0inmat.
Note: This question is the same as 1765: https://leetcode.com/problems/map-of-highest-peak/
Approach 1: Optimal
Intuition
- Multisource bfs
- Direction array because of grid
Algorithm
- Initialize an
ansmatrix initialized withINT_MAXandq - Push all the cell pos with the value of
0in mat - BFS on the queue,
- If the new distance is less than old distance
- change the distance
- Push the pos in the queue
- If the new distance is less than old distance
- Return ans;
Code
class Solution {
private:
const vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}};
public:
vector<vector<int>> updateMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int rows = mat.size(), cols = mat[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> ans(rows, vector<int>(cols, INT_MAX));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
// Initialize the queue with all '0' cells and set their distance to 0 in the answer matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 0) {
q.push({i, j});
ans[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
// Perform multi-source BFS from all '0' cells
while (!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (auto d : directions) {
int nr = r + d.first;
int nc = c + d.second;
if (nr < 0 || nr >= rows || nc < 0 || nc >= cols || ans[nr][nc] <= ans[r][c] + 1) continue;
ans[nr][nc] = ans[r][c] + 1;
q.push({nr, nc});
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: