733. Flood Fill
Question
You are given an image represented by an m x n grid of integers image, where image[i][j] represents the pixel value of the image. You are also given three integers sr, sc, and color. Your task is to perform a flood fill on the image starting from the pixel image[sr][sc].
To perform a flood fill:
- Begin with the starting pixel and change its color to
color. - Perform the same process for each pixel that is directly adjacent (pixels that share a side with the original pixel, either horizontally or vertically) and shares the same color as the starting pixel.
- Keep repeating this process by checking neighboring pixels of the updated pixels and modifying their color if it matches the original color of the starting pixel.
- The process stops when there are no more adjacent pixels of the original color to update.
Return the modified image after performing the flood fill.
Example 1:
Input: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1|1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]], sr = 1, sc = 1, color = 2
Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1|2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation:
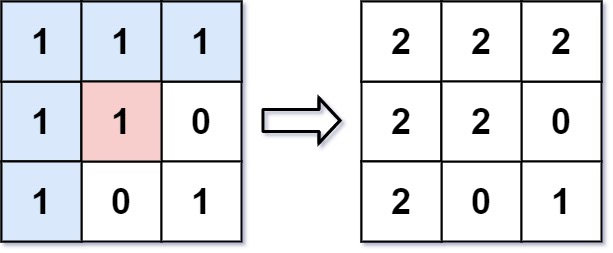
From the center of the image with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1) (i.e., the red pixel), all pixels connected by a path of the same color as the starting pixel (i.e., the blue pixels) are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not horizontally or vertically connected to the starting pixel.
Example 2:
Input: image = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0|0,0,0],[0,0,0]], sr = 0, sc = 0, color = 0
Output: [[0,0,0],[0,0,0|0,0,0],[0,0,0]]
Explanation:
The starting pixel is already colored with 0, which is the same as the target color. Therefore, no changes are made to the image.
Constraints:
m == image.lengthn == image[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500 <= image[i][j], color < 2160 <= sr < m0 <= sc < n
Approach 1: BFS
Intuition
- BFS
- Directions array
Algorithm
- Declare & intialize variables
- rows
- cols
- originalColor
- directions array
queue<pair<int, int>> q
- Edge case: if originalColor == color return image
- Put the
sr&scin queue & change the color to color - BFS loop while q is not empty
- Declare & initialize
r&cvariables - q.pop()
- Loop on directions array
- Create
nr&nc - Check if
nr&ncare in bounds and the cell color is the originalColor- Change the color
- Push the position in the queue
- Create
- Declare & initialize
- Return the image.
Code
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc,
int color) {
int rows = image.size(), cols = image[0].size();
int originalColor = image[sr][sc];
if (originalColor == color)
return image;
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({sr, sc});
image[sr][sc] = color;
while (!q.empty()) {
int r = q.front().first;
int c = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (auto direction : directions) {
int nr = r + direction.first;
int nc = c + direction.second;
if (nr >= 0 && nr < rows && nc >= 0 && nc < cols &&
image[nr][nc] == originalColor) {
q.push({nr, nc});
image[nr][nc] = color;
}
}
}
return image;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: DFS
Intuition
- DFS
- Recursion DSA
Algorithm
- Create a dfs function with base case at the top which modifies the image.
- Loop through the directions array
- Create new position
- As the conditions like if the pos is in bound is handled in the base case we can directly call the dfs on new position
- Return image frmo the floodfill function
Code
class Solution {
const vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {
{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
void dfs(int r, int c, int rows, int cols, int originalColor, int color,
vector<vector<int>>& image) {
if (r < 0 || r >= rows || c < 0 || c >= cols ||
originalColor == color || image[r][c] != originalColor)
return;
image[r][c] = color;
for (auto direction : directions) {
int rn = r + direction.first;
int rc = c + direction.second;
dfs(rn, rc, rows, cols, originalColor, color, image);
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> floodFill(vector<vector<int>>& image, int sr, int sc,
int color) {
int rows = image.size(), cols = image[0].size();
int originalColor = image[sr][sc];
if (originalColor == color)
return image;
dfs(sr, sc, rows, cols, originalColor, color, image);
return image;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
- n -> rows, m -> cols