787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
Question
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:
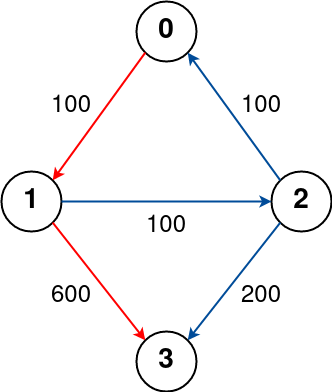
Input: n = 4, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200|0,1,100],[1,2,100],[2,0,100],[1,3,600],[2,3,200]], src = 0, dst = 3, k = 1
Output: 700
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 3 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 600 = 700.
Note that the path through cities [0,1,2,3] is cheaper but is invalid because it uses 2 stops.
Example 2:
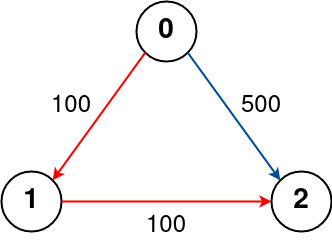
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500|0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1
Output: 200
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with at most 1 stop from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 100 + 100 = 200.
Example 3:
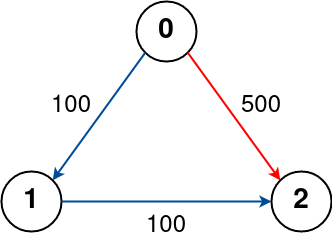
Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500|0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0
Output: 500
Explanation:
The graph is shown above.
The optimal path with no stops from city 0 to 2 is marked in red and has cost 500.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 104- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
Approach 1: BFS
Intuition
- Maintain no. of stops in the queue and total distance in another array
Algorithm
- Convert the edge list to adj list
- Declare a queue
queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> qcontaining {stops, {node, dist}} - Push the source node into the queue
- Declare and initialize the
distarray withINT_MAX - Update the source distance to 0
- While queue is not empty
- Get the node
- If the no. of stops is greater than k continue
- Loop over the neighbors of the node
- Check if the new cost of the neighbor is less than the existing cost
- Push the neighbor into the queue and update the distance
- Check if the new cost of the neighbor is less than the existing cost
- Check if the distance of source is equal to the
INT_MAXit was initialized with, if so return -1. - Else return the distance of the source from the
distarray.
Code
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
// 0. convert edge list to adj list
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> adj(n);
for (auto it: flights) {
adj[it[0]].push_back({it[1], it[2]});
}
// {stops, {node, dist}}
queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>> q;
q.push({0, {src, 0}});
vector<int> dist(n, 1e9);
dist[src] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto it = q.front();
q.pop();
int stops = it.first;
int node = it.second.first;
int cost = it.second.second;
if (stops > k) continue;
for (auto it : adj[node]) {
int adjNode = it.first;
int edW = it.second;
if (cost + edW < dist[adjNode] && stops <= k) {
dist[adjNode] = cost + edW;
q.push({stops + 1, {adjNode, cost + edW}});
}
}
}
if (dist[dst] == 1e9) return -1;
return dist[dst];
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Bellman Ford
Intuition
- At most k stops = at most k + 1 flights.
- Bellman–Ford guarantees shortest paths with at most
iedges after thei-th relaxation. - So we perform k + 1 rounds, each using the previous round’s distances.
- To prevent using updated values in the same iteration (which would allow more than
k + 1edges), we use a copy (temp).
Algorithm
- Initialize
dist[src] = 0and everything else = INF. - Repeat
k + 1times:- Create a copy
temp = dist. - For every flight
(u, v, w):- If
uis reachable, relax:
temp[v] = min(temp[v], dist[u] + w)
- If
- Assign
dist = temp.
- Create a copy
- Return
dist[dst]if reachable, else-1.
Code
class Solution {
public:
int findCheapestPrice(int n, vector<vector<int>>& flights, int src, int dst, int k) {
const int INF = 1e9;
// distance after i relaxations
vector<int> dist(n, INF);
dist[src] = 0;
// We only want paths with at most k+1 edges
for (int i = 0 ; i < k + 1 ; i++) {
vector<int> temp(dist); // keep previous layer stable
for (auto& edge: flights) {
int u = edge[0];
int v = edge[1];
int w = edge[2];
if (dist[u] == INF) continue; // unreachable so far
// Relax the edge but into temp ( to avoid over-relaxing)
temp[v] = min(temp[v], dist[u] + w);
}
dist = temp;
}
return dist[dst] == INF ? -1 : dist[dst];
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: