Find length of Loop GFG
| Attempt | Time Required |
|---|---|
| For notes | 15 min 48 sec |
Question
Given the head of a linked list, determine whether the list contains a loop. If a loop is present, return the number of nodes in the loop, otherwise return 0.

Note: 'c' is the position of the node which is the next pointer of the last node of the linkedlist. If c is 0, then there is no loop.
Examples:
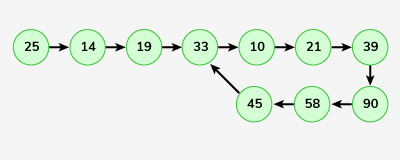
Input: LinkedList: 25->14->19->33->10->21->39->90->58->45, c = 4
Output: 7
Explanation: The loop is from 33 to 45. So length of loop is 33->10->21->39-> 90->58->45 = 7. The number 33 is connected to the last node of the linkedlist to form the loop because according to the input the 4th node from the beginning(1 based indexing)
will be connected to the last node for the loop.
Input: LinkedList: 5->4, c = 0
Output: 0
Explanation: There is no loop.

Expected Time Complexity: O(n)
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Constraints:
1 <= no. of nodes <= 106
0 <= node.data <=106
0 <= c<= n-1
Try more examples
Approach 1: Brute Force
Intuition
- Using hashing with
unordered_mapdata structure.
Algorithm
- Declare an
unordered_map<Node*, int> m - Declare & initialize
count = 1 - Declare & initialize
Node* currtohead - Loop through the LL using the
currnode.- If
currnode exists in the mapm- Return
count - m[curr], length of the loop
- Return
- Add
currto the mapmwith the value ofcount. - Increment
countby 1 curr = curr->next
- If
- Return 0, meaning there is no loop.
Code
class Solution {
public:
// Function to find the length of a loop in the linked list.
int countNodesinLoop(Node *head) {
unordered_map<Node*, int> m;
int count = 1;
Node* curr = head;
while (curr) {
if (m.find(curr) != m.end()) {
return count - m[curr];
}
m[curr] = count;
count++;
curr = curr->next;
}
return 0;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity:
Approach 2: Optimal
Intuition
- Floyd's tortoise hare cycle detection algorithm.
Algorithm
- Declare & initialize
Node* fast&Node* slowto head; - Loop through the LL till
fast != NULL && fast->next != NULLfast = fast->next->nextfast moves with 2 nodes at a time.slow = slow->nextslow moves with 1 node at a time.- if
fast == slow- Declare & initialize a
int count = 1 fast = fast->next- loop through the LL again till
fast != slowfast = fast->nextincrement fast by 1.count++
- Return
count
- Declare & initialize a
- Return 0;
Code
class Solution {
public:
// Function to find the length of a loop in the linked list.
int countNodesinLoop(Node *head) {
Node* fast = head;
Node* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow) {
int count = 1;
fast = fast->next;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast->next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: