Shortest Path in Undirected Graph GFG
- Link: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/problems/shortest-path-in-undirected-graph-having-unit-distance/0
Question
You are given an adjacency list, adj of Undirected Graph having unit weight of the edges, find the shortest path from src to all the vertex and if it is unreachable to reach any vertex, then return -1 for that vertex.
Examples :
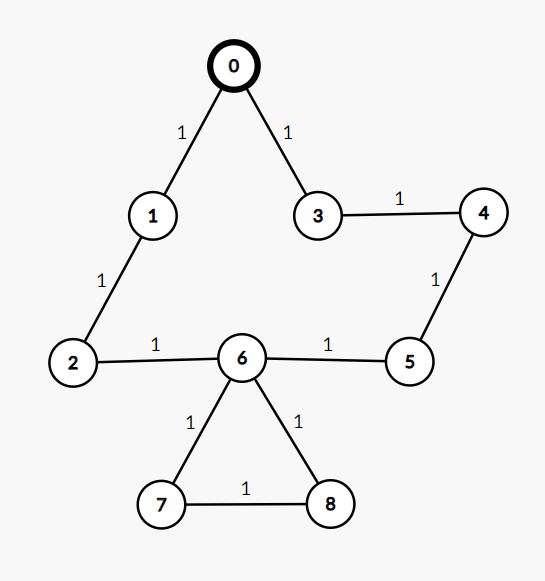
Input: adj[][] = 1, 3], [0, 2], [1, 6], [0, 4], [3, 5], [4, 6], [2, 5, 7, 8], [6, 8], [7, 6, src=0
Output: [0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4]
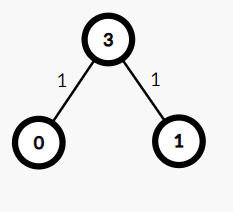
Input: adj[][]= 3], [3], [], [0, 1, src=3
Output: [1, 1, -1, 0]
Input: adj[][]= ], [], [], [4], [3], [], [, src=1
Output: [-1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1]
Constraint:
1<=adj.size()<=104
0<=edges<=adj.size()-1
Approach 1: Optimal
Intuition
- BFS
- Updating the distance if the current distance is less than the existing distance.
Algorithm
- Declare & initialize a distance array with INT_MAX.
- Declare queue of pair with first values as the node & second value as the distance from the source.
- Push the source into the queue with distance 0 & set distance for the source equal to 0.
- Loop till queue is not empty
- Get node & currDistance
- Pop the queue
- Loop over all its neighbors in the adj
- If the new distance (i.e, currDistance + 1) is less than the existing distance of that node in the distance array
- Replace the distance
- Push the node in the queue with the new distance
- If the new distance (i.e, currDistance + 1) is less than the existing distance of that node in the distance array
- Create a new array, initializing with -1. (ans)
- If the distance is not equal to the initial value of INT_MAX then update it in the ans array.
- Return
ans.
Code
class Solution {
public:
// Function to find the shortest path from source to all other nodes
vector<int> shortestPath(vector<vector<int>>& adj, int src) {
vector<int> distance(adj.size(), INT_MAX);
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({src, 0});
distance[src] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front().first;
int currDistance = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (auto neighbor : adj[node]) {
if (distance[neighbor] > currDistance + 1) {
distance[neighbor] = currDistance + 1;
q.push({neighbor, distance[neighbor]});
}
}
}
vector<int> ans(adj.size(), -1);
for(int i = 0;i<adj.size();i++) {
if(distance[i] != INT_MAX) {
ans[i] = distance[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Complexity Analysis
- Time Complexity:
- Space Complexity: